Card Classification
EECS 349 Machine Learning at Northwestern University
Final Report
Group Members’ Github and Contact:
Elton Cheng eltoncheng2017@u.northwestern.edu
Yuchen Rao yuchenrao2017@u.northwestern.edu
Weiyuan Deng weiyuandeng2017@u.northwestern.edu
Objective and Introduction
The goal of our project is to classify cards for a game of Blackjack. Given an image of a card, can the computer correctly identify it? (Ace, 2-10, Jack, Queen, King).
This task explores the idea of object recognition, a tool that is being used more and more in fields, such as self-driving cars and pick/place and sorting robots. Object recognition can provide more information for computers to make decisions on by being able to tell apart a red balloon to a stop sign, or a bottle of gatorade from dish soap.
We used playing cards specifically because for people, it is easy for us to classify each card, as we can tell them apart from the letters, numbers, artwork, etc. of the cards. The challenge for a computer to classify these cards comes in trying to recognize these features of the cards, and being able to interpret these features correctly. Each of the cards are unique enough that it can be a challenge for a computer to try and classify them all.

Dataset and Approach
At the beginning, the dataset contained 1040 images of one decks of 52 cards (Ace = 1, 2 ~ 10, Jack = 11, Queen = 12, and King = 13).
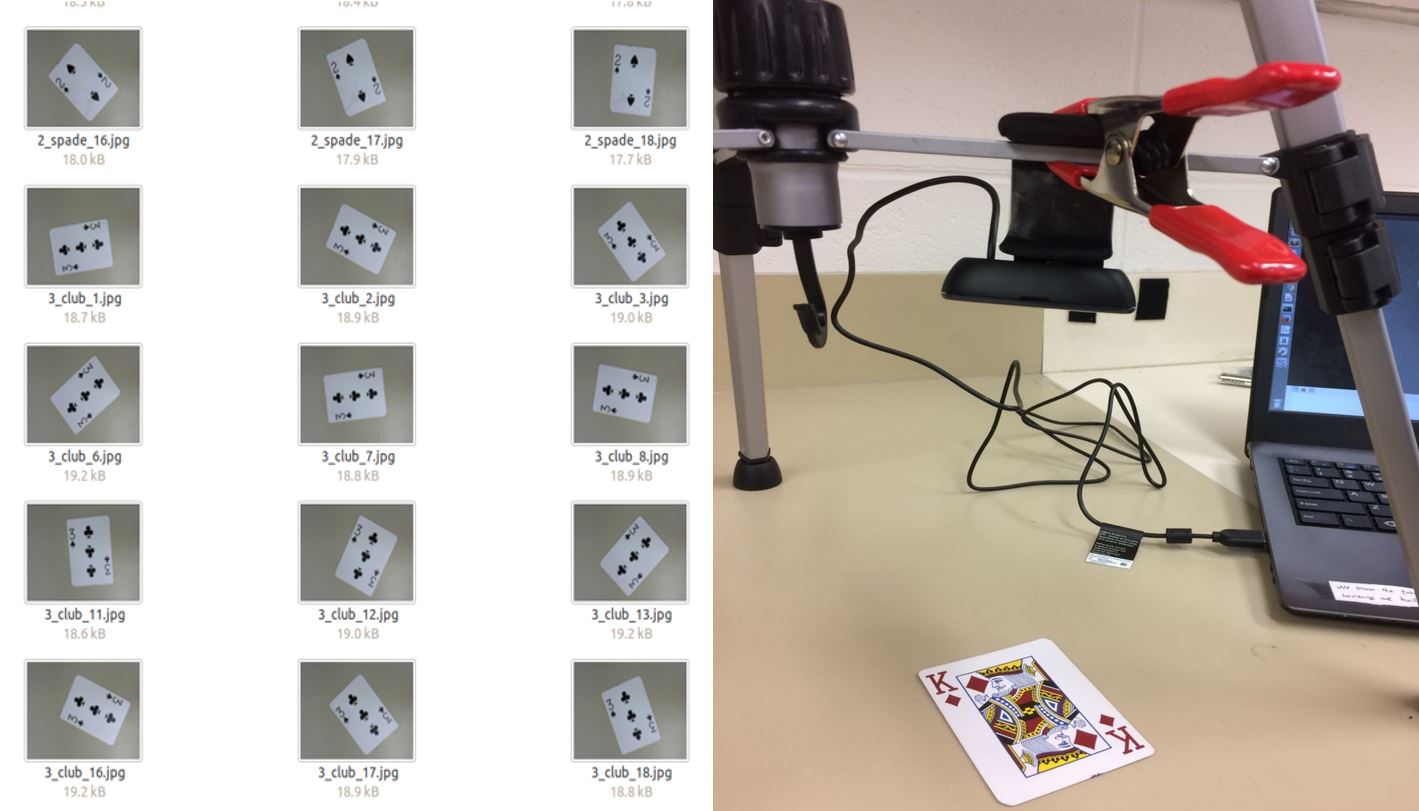

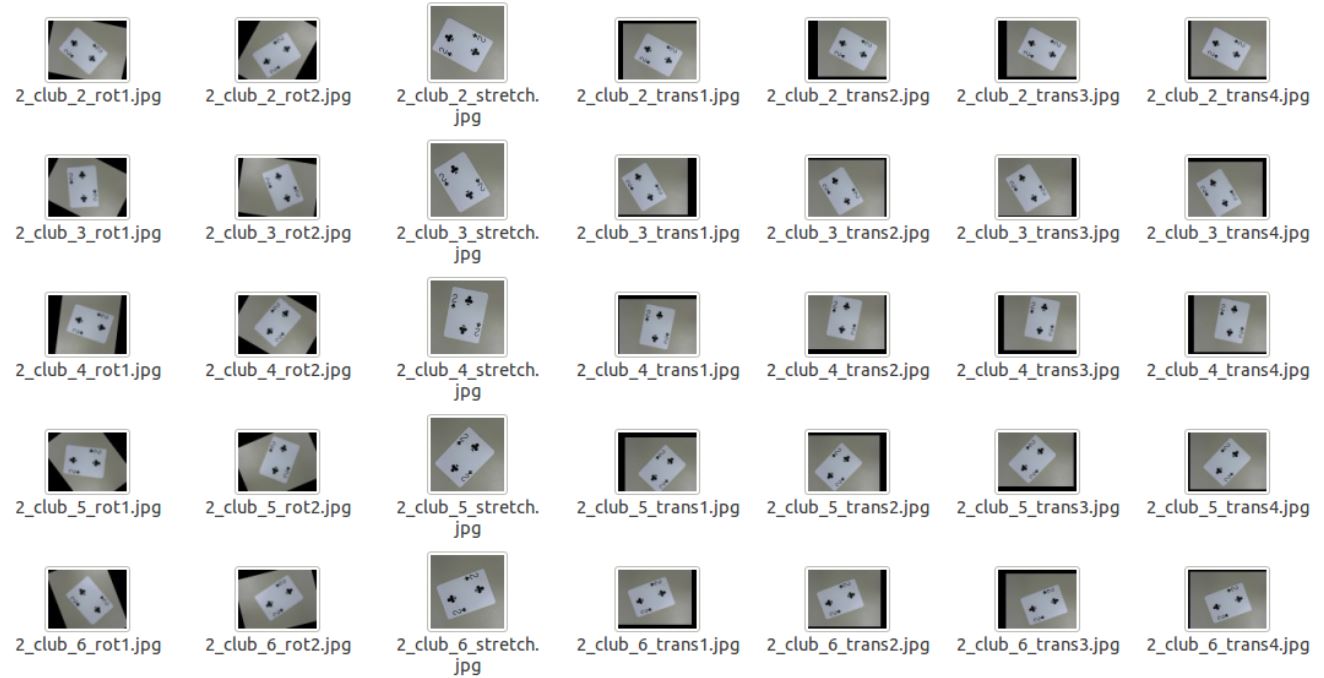
Each card has 20 pictures with the same background in different orientation. Then with data augmentation, we were able to add small random translations, rotations, zoom and scaling to expand the dataset to 10400 image (10 augments per image).

The learners in the project are 5-Nearest Neighbor, Support Vector Machine, 15-Layer Neural Net algorithm from Scikit-Learn and Convolutional Neural Net algorithm(CNN) from tflearn packages. The feature used for CNN is convolutional features, while features for other algorithms is Dense SIFT (DSIFT), a computer vision tool used to detect objects in an image.
10-fold cross validation is used to verify the accuracy of the model.
Results
With the augmented data set, the accuracy of SVM and CNN algorithms increased significantly. The best model we obtained was around 97% accuracy from the CNN algorithm. The features used for the best model used a convolutional filter size of 5.
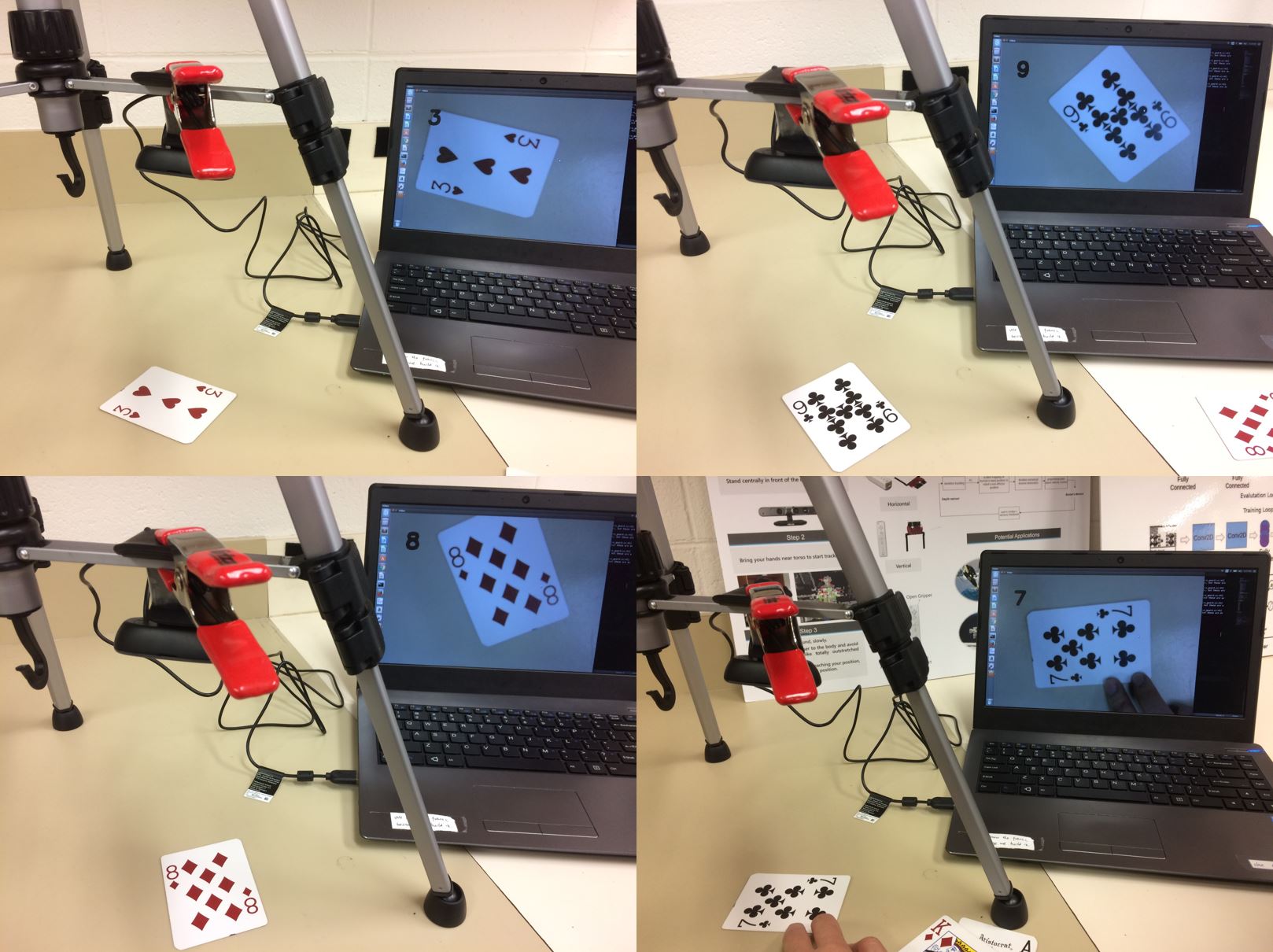
Demo Video
Here is a demo video of our final model.